Me323 and vw kubelwagen 2
Messerschmitt Me323 in winter 2
Me323 D-2 I/Kampfgeschwader z.b.V 323 X1L Sicily 1943 5
Me323 D-2 I/Kampfgeschwader z.b.V 323, X1L Sicily 1943 3
Messerschmitt Me323 and gun
Me 323 D-2 from I/Kampfgeschwader z.b.V 323, X1L Sicily 1943 2
Me 323 D-2 of the I/Kampfgeschwader z.b.V 323, X1L Sicily 1943. Early version still had two-bladed wooden propellers
Me323 and pak 40 gun
Messerschmitt Me323 gigant and sdkfz 7 halftrack
Me323 and vw kubelwagen photo
Me323 Gigant on the snow-covered airfield
Me 323 Gigant and opel blitz truck
Messerschmitt Me323 transport plane
Me323 D-2 I/Kampfgeschwader z.b.V 323, X1L Sicily 1943 4
Me 323 Gigant transport aircraft
Me323 winter
Me323 and pak40
Messerschmitt Me 323 D 2 Gigant
Me323 and wehrmacht truck
Me 323 in flight 8
Messerschmitt Me323
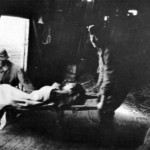
Wounded soldier being unloaded from the Me 323
Russia Me 323 Gigant transport plane
Ju 52 and Me 323
Me323 gigant
Me 323
Me 323 and Opel Maultier Italy
Me323 Gigant front
Sdkfz 8 towing a Me 323
Damaged Me323
Renault UE being unloaded from a Me 323
Faun ZR 567 towing a Me 323
Me 323 Gigant, 1944
Me 110 and Me 323
Me 323 Gigant of the 1/TG 5, Tunisia
German aircraft wrecks at El Aouina May 1943
Me 323 of the TG 5 Eastern Front
Me 323 under attack off Corsica 1943
Me 323 D-1 W.Nr. 1220 DT+IT of the II/TG 5
Me 323D wreck Tunis May 1943
Messerschmitt Me323
Two wing turrets of Me 323 Gigant
Me323 Gigant Sicily
Me 323, Focke-Wulf Fw58 “Weihe” and Fw190 in hangar
Unloading truck from a Gigant
Me323D wreck
Me 323E-2
Glider Me321 of the GS-Kommando 2, Crimea 1943
Me323 Gigant RF+XM in flight
Me323E-2/WT and Romanian Bf109G coded White 43a
Wing gun positions
Flak 88 being loaded into the cargo bay hold of a Gigant
Me323 in color
Me 323 of II/TG 5 30 July 1943
Opel Blitz
Me 323 in Russia
Me 323 in flight color photo 7
Messerschmitt Me323 on the ground airfield
Italy Flugzeug Me 323 Gigant Kanone
The cockpit interior of the Messerschmitt Me 323 Gigant
front cargo bay doors open for loading
Cargo compartment
German soldiers stand before boarding
Luftwaffe fuel truck with trailer
Me323 at Grosseto
Opel Blitz Kfz 385 Fuel Truck next to Me 323
Me 323 in color
Loading of a halftrack and 15 cm aFH 18 onto a Me323
Right side view
Me323 code C8+FN Mucke, 1942/1943
Wounded soldier being unloaded from a Me323
Wounded soldiers being unloaded from a Me323 transport plane
Me 323 at a captured Soviet airfield
Messerschmitt Me323 – Gnome-Rhône 14N engines
Messerschmitt Me321
Messerschmitt Me323
me323 800px Gigant italie 1943
Tunesien Flugzeug Me 323 Gigant Innenraum
Me323 Gigant Romania
Remains of a Me323
Me 323 is prepared for its next operation
me323 561 1142 21 Grosseto Flugzeug Me 323 Verwundetentransport
Me 321 take off
Messerschmitt Gigant 323 side
Me323
me323 photo in color
me323
me323
Messerschmitt Me323
Me 323 unloading a Marder II
Messerschmitt Me 323 in flight
me323 3
Me323D wreck Tunis May 1943
Messerschmitt Me323
Four-engined Messerschmitt Me 323C in flight
me323 4
Me 323 Gigant
Messerschmitt Me 323 engine maintenance
Me323 warming-up its engines, Italy Pisa
Me 323 of the Feldwerft vb (MOT) 10
Messerschmitt Me 323 and Bf109 from JG 53
Me 323 at rest
Messerschmitt Me323 on the ground
Me 323 Honig
Messerschmitt Me323 ground crew loads 15cm sFH18
Messerschmitt Me 323 Gigant was a largest land-based German military transport aircraft of World War II. It was a powered variant of the Me321 glider.
Design and Structure
- Type: Six-engined transport monoplane.
- Wings:
- Configuration: High-wing, semi-cantilever with a wide-span center-section supported by a single strut on each side.
- Structure:
- Center-section: Plywood-covered with steel tube members and N-braces, creating a rectangular girder spar structure.
- Outer Sections: Continuation of the taper with dihedral angle, plywood covering the leading edge and back to the spar, with the rest fabric-covered.
- Control Surfaces: Entire trailing edge is hinged; outer portions serve as ailerons and inner sections as flaps. These are carried on steel tube outriggers from the main spar. The ailerons have combined servo and trim-tabs, aided by an electric servo-motor in each wing.
- Fuselage:
- Construction: Rectangular welded steel tubing framework covered with fabric over a secondary wood fairing structure.
- Floor: Main floor in the forward fuselage supported by substantial cross girders.
- Tail Unit:
- Type: Braced monoplane with an all-wood structure. The tail unit and the portion of the fuselage it attaches to can hinge hydraulically, adjusting tail incidence from +2.5 to -5 degrees.
Landing Gear
- Type: Multi-wheel setup with ten wheels designed to navigate ground obstacles like a caterpillar track.
- Arrangement: Tandem alongside the lower edge of the fuselage, housed in elongated paddle-box type fairings. The wheels are sprung by coil springs, keeping the aircraft horizontal regardless of load distribution.
- Features: Six main wheels with pneumatic brakes.
Power Plant
- Engines: Six Gnome-Rhône 14N 48/49 fourteen-cylinder radial air-cooled engines, each producing 990 hp at 12,200 ft (3,720 m).
- Propellers: Variable-pitch metal or fixed-pitch wooden airscrews, with port engines as L.H. tractors and starboard engines as R.H. tractors.
- Fuel Capacity: 2,364 Imperial gallons (10,740 liters) in twelve self-sealing fuel tanks in the wings, with some versions having additional tanks in the freight compartment.
- Engine Control: Two flight engineers, each controlling three engines on their side of the fuselage from positions within the wing roots.
- Rocket Assist: Provision for four rockets under the wings for assisted take-off.
Accommodation
- Crew: Typically five, including two pilots, two flight engineers, and one radio operator.
- Cockpit: Armored, seating two pilots side-by-side with dual controls in front of the wing’s leading edge.
- Engineers: Positioned in the leading edge of the wings.
- Main Hold: 36 ft long, 10 ft 3 in wide, and 11 ft high, occupying the full cross-section of the fuselage with a cubic capacity of 3,530 cu ft. The nose can split into two outwardly-hinging doors for loading.
Specifications:
variant | Me 323 V-1 (prototype of Me 323 C) | Me 323 D | Me 323 E-2 | Me 323 E-2/WT (“gunship”) |
crew | 8 | 10 | 12 | 17 |
wingspan (m) | 55,00 | 55,00 | 55,00 | 55,00 |
lenght (m) | 28,15 | 28,15 | 28,15 | 28,15 |
height (m) | 9,60 | 9,60 | 9,60 | 9,60 |
wing area (m2) | 300,00 | 300,00 | 300,00 | 300,00 |
gross weight (kg) | 25400 | 27330 | 29000 | 32000 |
normal take-off weight (kg) | 34000 | 43000 | 48000 | 40000 |
max take-off weight (kg) | 36000 | 45000 | 50000 | 42000 |
payload (kg) | 6000 – 8000 | 10000 – 12000 | 9000 – 10000 | – |
capacity (troops) | 130 | 120 | – | |
engines | 4 x Gnome-Rhône 14N-48/49, 1164 hp | 6 x Gnome-Rhône 14N-48/49, 1164 hp | 6 x Gnome-Rhône 14N-48/49, 1164 hp | 6 x Gnome-Rhône 14N-48/49, 1164 hp |
max speed (km/h) | 220 | 280 | 252 | 255 |
cruising speed (km/h) | 170 | 186 at 1500m | 208 at 1500m | 225 at 1500m |
landing speed (km/h) | 115 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
service ceiling (m) | 2000 | 4500 | 4200 | 4500 |
range (km) | 1100 | 750-1100 | 1100-1300 | 1000-1200 |
endurance | 6h | 4,5h | 5,5h | 5h |
take off run (m) | 900 | 850 | 800 | 800 |
landing run (m) | 500 | 600 | 700 | 600 |
armament | 4 x MG15 | 2 x MG151/20, 5 x MG131 | 11 x MG151/20, 4x MG131 |